一、概述
1.Pod 水平自动扩缩
Pod 水平自动扩缩(Horizontal Pod Autoscaler) 可以基于 CPU 利用率自动扩缩 ReplicationController、Deployment、ReplicaSet 和 StatefulSet 中的 Pod 数量。 除了 CPU 利用率,也可以基于其他应程序提供的 自定义度量指标 来执行自动扩缩。 Pod 自动扩缩不适用于无法扩缩的对象,比如 DaemonSet。
自定义度量指标:
https://github.com/kubernetes/community/blob/master/contributors/design-proposals/instrumentation/custom-metrics-api.md
Pod 水平自动扩缩特性由 Kubernetes API 资源和控制器实现。资源决定了控制器的行为。 控制器会周期性地调整副本控制器或 Deployment 中的副本数量,以使得类似 Pod 平均 CPU 利用率、平均内存利用率这类观测到的度量值与用户所设定的目标值匹配。
Pod 水平自动扩缩器的实现是一个控制回路,由控制器管理器的 --horizontal-pod-autoscaler-sync-period 参数指定周期(默认值为 15 秒)。
每个周期内,控制器管理器根据每个 HorizontalPodAutoscaler 定义中指定的指标查询资源利用率。 控制器管理器可以从资源度量指标 API(按 Pod 统计的资源用量)和自定义度量指标 API(其他指标)获取度量值。
-
对于按 Pod 统计的资源指标(如 CPU),控制器从资源指标 API 中获取每一个 HorizontalPodAutoscaler 指定的 Pod 的度量值,如果设置了目标使用率, 控制器获取每个 Pod 中的容器资源使用情况,并计算资源使用率。 如果设置了 target 值,将直接使用原始数据(不再计算百分比)。 接下来,控制器根据平均的资源使用率或原始值计算出扩缩的比例,进而计算出目标副本数。
需要注意的是,如果 Pod 某些容器不支持资源采集,那么控制器将不会使用该 Pod 的 CPU 使用率。 下面的算法细节章节将会介绍详细的算法。
-
如果 Pod 使用自定义指示,控制器机制与资源指标类似,区别在于自定义指标只使用 原始值,而不是使用率。
-
如果 Pod 使用对象指标和外部指标(每个指标描述一个对象信息)。 这个指标将直接根据目标设定值相比较,并生成一个上面提到的扩缩比例。 在
autoscaling/v2beta2版本 API 中,这个指标也可以根据 Pod 数量平分后再计算。
通常情况下,控制器将从一系列的聚合 API(metrics.k8s.io、custom.metrics.k8s.io 和 external.metrics.k8s.io)中获取度量值。 metrics.k8s.io API 通常由 Metrics 服务器(需要额外启动)提供。 可以从 metrics-server 获取更多信息。 另外,控制器也可以直接从 Heapster 获取指标。
1
2
3
4
# 说明:
FEATURE STATE: Kubernetes 1.11 [deprecated]
自 Kubernetes 1.11 起,从 Heapster 获取指标特性已废弃。
关于指标 API 更多信息,请参考度量值指标 API 的支持。
自动扩缩控制器使用 scale 子资源访问相应可支持扩缩的控制器(如副本控制器、 Deployment 和 ReplicaSet)。 scale 是一个可以动态设定副本数量和检查当前状态的接口。 关于 scale 子资源的更多信息,请参考这里
1.Metrics 服务器
Metrics 服务器 是集群范围资源用量数据的聚合器。 默认情况下,在由 kube-up.sh 脚本创建的集群中会以 Deployment 的形式被部署。 如果你使用其他 Kubernetes 安装方法,则可以使用提供的 部署组件 components.yaml 来部署。
Metric 服务器从每个节点上的 kubelet 公开的 Summary API 中采集指标信息。 该 API 通过 Kubernetes 聚合器 注册到主 API 服务器上。
在设计文档 中可以了解到有关 Metrics 服务器的更多信息。
1
2
# metrics-server:
https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server
2.算法细节
从最基本的角度来看,Pod 水平自动扩缩控制器根据当前指标和期望指标来计算扩缩比例。
1
期望副本数 = ceil[当前副本数 * (当前指标 / 期望指标)]
例如,当前度量值为 200m,目标设定值为 100m,那么由于 200.0/100.0 == 2.0, 副本数量将会翻倍。 如果当前指标为 50m,副本数量将会减半,因为50.0/100.0 == 0.5。 如果计算出的扩缩比例接近 1.0 (根据--horizontal-pod-autoscaler-tolerance 参数全局配置的容忍值,默认为 0.1), 将会放弃本次扩缩。
如果 HorizontalPodAutoscaler 指定的是 targetAverageValue 或 targetAverageUtilization, 那么将会把指定 Pod 度量值的平均值做为 currentMetricValue。 然而,在检查容忍度和决定最终扩缩值前,我们仍然会把那些无法获取指标的 Pod 统计进去。
所有被标记了删除时间戳(Pod 正在关闭过程中)的 Pod 和失败的 Pod 都会被忽略。
如果某个 Pod 缺失度量值,它将会被搁置,只在最终确定扩缩数量时再考虑。
当使用 CPU 指标来扩缩时,任何还未就绪(例如还在初始化)状态的 Pod 或 最近的指标 度量值采集于就绪状态前的 Pod,该 Pod 也会被搁置。
由于受技术限制,Pod 水平扩缩控制器无法准确的知道 Pod 什么时候就绪, 也就无法决定是否暂时搁置该 Pod。 --horizontal-pod-autoscaler-initial-readiness-delay 参数(默认为 30s)用于设置 Pod 准备时间, 在此时间内的 Pod 统统被认为未就绪。 --horizontal-pod-autoscaler-cpu-initialization-period 参数(默认为5分钟) 用于设置 Pod 的初始化时间, 在此时间内的 Pod,CPU 资源度量值将不会被采纳。
在排除掉被搁置的 Pod 后,扩缩比例就会根据 currentMetricValue/desiredMetricValue 计算出来。
如果缺失任何的度量值,我们会更保守地重新计算平均值, 在需要缩小时假设这些 Pod 消耗了目标值的 100%, 在需要放大时假设这些 Pod 消耗了 0% 目标值。 这可以在一定程度上抑制扩缩的幅度。
此外,如果存在任何尚未就绪的 Pod,我们可以在不考虑遗漏指标或尚未就绪的 Pod 的情况下进行扩缩, 我们保守地假设尚未就绪的 Pod 消耗了期望指标的 0%,从而进一步降低了扩缩的幅度。
在扩缩方向(缩小或放大)确定后,我们会把未就绪的 Pod 和缺少指标的 Pod 考虑进来再次计算使用率。 如果新的比率与扩缩方向相反,或者在容忍范围内,则跳过扩缩。 否则,我们使用新的扩缩比例。
注意,平均利用率的原始值会通过 HorizontalPodAutoscaler 的状态体现( 即使使用了新的使用率,也不考虑未就绪 Pod 和 缺少指标的 Pod)。
如果创建 HorizontalPodAutoscaler 时指定了多个指标, 那么会按照每个指标分别计算扩缩副本数,取最大值进行扩缩。 如果任何一个指标无法顺利地计算出扩缩副本数(比如,通过 API 获取指标时出错), 并且可获取的指标建议缩容,那么本次扩缩会被跳过。 这表示,如果一个或多个指标给出的 desiredReplicas 值大于当前值,HPA 仍然能实现扩容。
最后,在 HPA 控制器执行扩缩操作之前,会记录扩缩建议信息。 控制器会在操作时间窗口中考虑所有的建议信息,并从中选择得分最高的建议。 这个值可通过 kube-controller-manager 服务的启动参数 --horizontal-pod-autoscaler-downscale-stabilization 进行配置, 默认值为 5 分钟。 这个配置可以让系统更为平滑地进行缩容操作,从而消除短时间内指标值快速波动产生的影响。
3.kubectl 也支持Horizontal Pod Autoscaler
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 查看autoscalers列表
kubectl get hpa
# 查看具体描述
kubectl describe hpa
# 删除autoscaler
kubectl delete hpa
# 示例:以下命名将会为副本集foo创建一个autoscaler,并设置目标CPU利用率为80%,副本数在2~5之间
kubectl autoscale rs foo --min=2 --max=5 --cpu-percent=80
2.容器管理资源
当你定义 Pod 时可以选择性地为每个 容器设定所需要的资源数量。 最常见的可设定资源是 CPU 和内存(RAM)大小;此外还有其他类型的资源。
当你为 Pod 中的 Container 指定了资源 请求 时,调度器就利用该信息决定将 Pod 调度到哪个节点上。 当你还为 Container 指定了资源 约束 时,kubelet 就可以确保运行的容器不会使用超出所设约束的资源。 kubelet 还会为容器预留所 请求 数量的系统资源,供其使用。
请求和约束
如果 Pod 运行所在的节点具有足够的可用资源,容器可能(且可以)使用超出对应资源 request 属性所设置的资源量。不过,容器不可以使用超出其资源 limit 属性所设置的资源量。
例如,如果你将容器的 memory 的请求量设置为 256 MiB,而该容器所处的 Pod 被调度到一个具有 8 GiB 内存的节点上,并且该节点上没有其他 Pods 运行,那么该容器就可以尝试使用更多的内存。
如果你将某容器的 memory 约束设置为 4 GiB,kubelet (和 容器运行时) 就会确保该约束生效。 容器运行时会禁止容器使用超出所设置资源约束的资源。 例如:当容器中进程尝试使用超出所允许内存量的资源时,系统内核会将尝试申请内存的进程终止, 并引发内存不足(OOM)错误。
约束值可以以被动方式来实现(系统会在发现违例时进行干预),或者通过强制生效的方式实现 (系统会避免容器用量超出约束值)。不同的容器运行时采用不同方式来实现相同的限制。
说明:
如果某 Container 设置了自己的内存限制但未设置内存请求,Kubernetes 自动为其设置与内存限制相匹配的请求值。类似的,如果某 Container 设置了 CPU 限制值但未设置 CPU 请求值,则 Kubernetes 自动为其设置 CPU 请求 并使之与 CPU 限制值匹配。
资源类型
CPU 和内存都是资源类型。每种资源类型具有其基本单位。 CPU 表达的是计算处理能力,其单位是 Kubernetes CPUs。 内存的单位是字节。 如果你使用的是 Kubernetes v1.14 或更高版本,则可以指定巨页(Huge Page)资源。 巨页是 Linux 特有的功能,节点内核在其中分配的内存块比默认页大小大得多。
例如,在默认页面大小为 4KiB 的系统上,你可以指定约束 hugepages-2Mi: 80Mi。 如果容器尝试分配 40 个 2MiB 大小的巨页(总共 80 MiB ),则分配请求会失败。
说明:
你不能过量使用
hugepages- *资源。 这与memory和cpu资源不同。
CPU 和内存统称为计算资源,或简称为资源。 计算资源的数量是可测量的,可以被请求、被分配、被消耗。 它们与 API 资源 不同。 API 资源(如 Pod 和 Service)是可通过 Kubernetes API 服务器读取和修改的对象。
Pod 和 容器的资源请求和约束
Pod 中的每个容器都可以指定以下的一个或者多个值:
spec.containers[].resources.limits.cpuspec.containers[].resources.limits.memoryspec.containers[].resources.limits.hugepages-<size>spec.containers[].resources.requests.cpuspec.containers[].resources.requests.memoryspec.containers[].resources.requests.hugepages-<size>
尽管请求和限制值只能在单个容器上指定,我们仍可方便地计算出 Pod 的资源请求和约束。 Pod 对特定资源类型的请求/约束值是 Pod 中各容器对该类型资源的请求/约束值的总和。
Kubernetes 中的资源单位
CPU 的含义
CPU 资源的约束和请求以 cpu 为单位。
Kubernetes 中的一个 cpu 等于云平台上的 1 个 vCPU/核和裸机 Intel 处理器上的 **1 个超线程 **。
你也可以表达带小数 CPU 的请求。spec.containers[].resources.requests.cpu 为 0.5 的 Container 肯定能够获得请求 1 CPU 的容器的一半 CPU 资源。表达式 0.1 等价于表达式 100m, 可以看作 “100 millicpu”。有些人说成是“一百毫 cpu”,其实说的是同样的事情。 具有小数点(如 0.1)的请求由 API 转换为 100m;最大精度是 1m。 因此,或许你应该优先考虑使用 100m 的形式。
CPU 总是按绝对数量来请求的,不可以使用相对数量; 0.1 的 CPU 在单核、双核、48 核的机器上的意义是一样的。
CPU 单位
CPU 资源以 CPU 单位度量。Kubernetes 中的一个 CPU 等同于:
- 1 个 AWS vCPU
- 1 个 GCP核心
- 1 个 Azure vCore
- 裸机上具有超线程能力的英特尔处理器上的 1 个超线程
小数值是可以使用的。一个请求 0.5 CPU 的容器保证会获得请求 1 个 CPU 的容器的 CPU 的一半。 你可以使用后缀 m 表示毫。例如 100m CPU、100 milliCPU 和 0.1 CPU 都相同。 精度不能超过 1m。
CPU 请求只能使用绝对数量,而不是相对数量。0.1 在单核、双核或 48 核计算机上的 CPU 数量值是一样的。
内存的含义
内存的约束和请求以字节为单位。你可以使用以下后缀之一以一般整数或定点数字形式来表示内存: E、P、T、G、M、k。你也可以使用对应的 2 的幂数:Ei、Pi、Ti、Gi、Mi、Ki。 例如,以下表达式所代表的是大致相同的值:
1
128974848、129e6、129M、123Mi
下面是个例子。
以下 Pod 有两个 Container。每个 Container 的请求为 0.25 cpu 和 64MiB(226 字节)内存, 每个容器的资源约束为 0.5 cpu 和 128MiB 内存。 你可以认为该 Pod 的资源请求为 0.5 cpu 和 128 MiB 内存,资源限制为 1 cpu 和 256MiB 内存。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: frontend
spec:
containers:
- name: app
image: images.my-company.example/app:v4
env:
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: "password"
resources:
requests:
memory: "64Mi"
cpu: "250m"
limits:
memory: "128Mi"
cpu: "500m"
- name: log-aggregator
image: images.my-company.example/log-aggregator:v6
resources:
requests:
memory: "64Mi"
cpu: "250m"
limits:
memory: "128Mi"
cpu: "500m"
内存单位
内存资源的基本单位是字节(byte)。你可以使用这些后缀之一,将内存表示为 纯整数或定点整数:E、P、T、G、M、K、Ei、Pi、Ti、Gi、Mi、Ki。 例如,下面是一些近似相同的值:
1
128974848, 129e6, 129M , 123Mi
带资源请求的 Pod 如何调度
当你创建一个 Pod 时,Kubernetes 调度程序将为 Pod 选择一个节点。 每个节点对每种资源类型都有一个容量上限:可为 Pod 提供的 CPU 和内存量。 调度程序确保对于每种资源类型,所调度的容器的资源请求的总和小于节点的容量。 请注意,尽管节点上的实际内存或 CPU 资源使用量非常低,如果容量检查失败, 调度程序仍会拒绝在该节点上放置 Pod。 当稍后节点上资源用量增加,例如到达请求率的每日峰值区间时,节点上也不会出现资源不足的问题。
带资源约束的 Pod 如何运行
当 kubelet 启动 Pod 中的 Container 时,它会将 CPU 和内存约束信息传递给容器运行时。
当使用 Docker 时:
-
spec.containers[].resources.requests.cpu先被转换为可能是小数的基础值,再乘以 1024。 这个数值和 2 的较大者用作docker run命令中的--cpu-shares标志的值。 -
spec.containers[].resources.limits.cpu先被转换为 millicore 值,再乘以 100。 其结果就是每 100 毫秒内容器可以使用的 CPU 时间总量。在此期间(100ms),容器所使用的 CPU 时间不会超过它被分配的时间。说明: 默认的配额(Quota)周期为 100 毫秒。CPU 配额的最小精度为 1 毫秒。
-
spec.containers[].resources.limits.memory被转换为整数值,作为docker run命令中的--memory参数值。
如果 Container 超过其内存限制,则可能会被终止。如果容器可重新启动,则与所有其他类型的 运行时失效一样,kubelet 将重新启动容器。
如果一个 Container 内存用量超过其内存请求值,那么当节点内存不足时,容器所处的 Pod 可能被逐出。
每个 Container 可能被允许也可能不被允许使用超过其 CPU 约束的处理时间。 但是,容器不会由于 CPU 使用率过高而被杀死。
要确定 Container 是否会由于资源约束而无法调度或被杀死,请参阅疑难解答 部分。
监控计算和内存资源用量
Pod 的资源使用情况是作为 Pod 状态的一部分来报告的。
如果为集群配置了可选的 监控工具, 则可以直接从 指标 API 或者监控工具获得 Pod 的资源使用情况。
资源监控工具
要扩展应用程序并提供可靠的服务,你需要了解应用程序在部署时的行为。 你可以通过检测容器检查 Kubernetes 集群中的应用程序性能, Pods, 服务 和整个集群的特征。 Kubernetes 在每个级别上提供有关应用程序资源使用情况的详细信息。 此信息使你可以评估应用程序的性能,以及在何处可以消除瓶颈以提高整体性能。
在 Kubernetes 中,应用程序监控不依赖单个监控解决方案。 在新集群上,你可以使用资源度量或 完整度量管道来收集监视统计信息。
资源度量管道
资源指标管道提供了一组与集群组件,例如 Horizontal Pod Autoscaler 控制器以及 kubectl top 实用程序相关的有限度量。 这些指标是由轻量级的、短期、内存存储的 metrics-server 收集的, 通过 metrics.k8s.io 公开。
度量服务器发现集群中的所有节点,并且查询每个节点的 kubelet 以获取 CPU 和内存使用情况。 Kubelet 充当 Kubernetes 主节点与节点之间的桥梁,管理机器上运行的 Pod 和容器。 kubelet 将每个 Pod 转换为其组成的容器,并在容器运行时通过容器运行时接口 获取各个容器使用情况统计信息。 kubelet 从集成的 cAdvisor 获取此信息,以进行旧式 Docker 集成。 然后,它通过 metrics-server Resource Metrics API 公开聚合的 pod 资源使用情况统计信息。 该 API 在 kubelet 的经过身份验证和只读的端口上的 /metrics/resource/v1beta1 中提供。
完整度量管道
一个完整度量管道可以让你访问更丰富的度量。 Kubernetes 还可以根据集群的当前状态,使用 Pod 水平自动扩缩器等机制, 通过自动调用扩展或调整集群来响应这些度量。 监控管道从 kubelet 获取度量值,然后通过适配器将它们公开给 Kubernetes, 方法是实现 custom.metrics.k8s.io 或 external.metrics.k8s.io API。
Prometheus 是一个 CNCF 项目,可以原生监控 Kubernetes、 节点和 Prometheus 本身。 完整度量管道项目不属于 CNCF 的一部分,不在 Kubernetes 文档的范围之内。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 官方参考
为容器管理资源
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/
为容器和 Pods 分配 CPU 资源
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/assign-cpu-resource/
为容器和 Pod 分配内存资源
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/assign-memory-resource/
3.容器资源限制
3.1.资源的限制类型
Kubernetes采用request和limit两种限制类型来对资源进行分配。 • request(资源需求):即运行Pod的节点必须满足运行Pod的最基本需求才能 运行Pod。 • limit(资源限额):即运行Pod期间,可能内存使用量会增加,那最多能使用多少内存,这就是资源限额。
资源类型: • CPU 的单位是核心数,内存的单位是字节。 • 一个容器申请0.5个CPU,就相当于申请1个CPU的一半,你也可以加个后缀 m 表示千分之一的概念。比如说100m的CPU,100豪的CPU和0.1个CPU都是一样的。 内存单位: • K、M、G、T、P、E #通常是以1000为换算标准的。 • Ki、Mi、Gi、Ti、Pi、Ei #通常是以1024为换算标准的。
3.2.Pod资源限制
备注:CPU单位换算:100m CPU,100 milliCPU 和 0.1 CPU 都相同;精度不能超过 1m。1000m CPU = 1 CPU。
1
2
3
4
# 官网地址
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/assign-cpu-resource/
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/assign-memory-resource/
Kubernetes对资源的限制实际上是通过cgroup来控制的,cgroup是容器的一组用来控制内核如何运行进程的相关属性集合。针对内存、CPU和各种设备都有对应的cgroup。
默认情况下,Pod运行没有CPU和内存的限额。这意味着系统中的任何Pod将能够像执行Pod所在节点机器一样,可以消耗足够多的CPU和内存。一般会针对某些应用的Pod资源进行资源限制,这个资源限制是通过resources的requests【要分配的资源】和limits【最大使用资源】来实现的。
CPU资源限制示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# cat cpu-request-limit.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: cpu-demo
namespace: cpu-example
spec:
containers:
- name: cpu-demo-ctr
image: vish/stress
resources:
limits:
cpu: "1"
requests:
cpu: "0.5"
args:
- -cpus
- "2"
配置文件的 args 部分提供了容器启动时的参数。-cpus “2”参数告诉容器尝试使用 2 个 CPU。
内存资源限制示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# memory-request-limit.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: memory-demo
namespace: mem-example
spec:
containers:
- name: memory-demo-ctr
image: polinux/stress
resources:
limits:
memory: "200Mi"
requests:
memory: "100Mi"
command: ["stress"]
args: ["--vm", "1", "--vm-bytes", "150M", "--vm-hang", "1"]
配置文件的 args 部分提供了容器启动时的参数。 “–vm-bytes”, “150M” 参数告知容器尝试分配 150 MiB 内存。不允许args中的启动内存大于limits限制内存。
3.3.namespace资源限制
备注:CPU单位换算:100m CPU,100 milliCPU 和 0.1 CPU 都相同;精度不能超过 1m。1000m CPU = 1 CPU。
1
2
3
# 官网地址
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/manage-resources/
为命名空间配置内存和 CPU 配额 怎么为命名空间设置容器可用的内存和 CPU 总量。你可以通过 ResourceQuota 对象设置配额,使用 ResourceQuota 限制命名空间中所有容器的内存请求总量、内存限制总量、CPU 请求总量和CPU 限制总量。
如果你想对单个容器而不是所有容器进行限制,就请使用 LimitRange。
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# cat quota-mem-cpu.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: mem-cpu-demo
spec:
hard:
requests.cpu: "1"
requests.memory: 1Gi
limits.cpu: "2"
limits.memory: 2Gi
应用如下【命名空间quota-mem-cpu-example已提前创建完毕】:
kubectl create -f quota-mem-cpu.yaml –namespace=quota-mem-cpu-example
查看 ResourceQuota 详情:
kubectl get resourcequota mem-cpu-demo –namespace=quota-mem-cpu-example –output=yaml
输出部分结果如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
spec:
hard:
limits.cpu: "2"
limits.memory: 2Gi
requests.cpu: "1"
requests.memory: 1Gi
status:
hard:
limits.cpu: "2"
limits.memory: 2Gi
requests.cpu: "1"
requests.memory: 1Gi
used:
limits.cpu: "0"
limits.memory: "0"
requests.cpu: "0"
requests.memory: "0"
ResourceQuota 在 quota-mem-cpu-example 命名空间中设置了如下要求:
- 每个容器必须有内存请求和限制,以及 CPU 请求和限制。
- 所有容器的内存请求总和不能超过1 GiB。
- 所有容器的内存限制总和不能超过2 GiB。
- 所有容器的 CPU 请求总和不能超过1 cpu。
- 所有容器的 CPU 限制总和不能超过2 cpu。
为命名空间配置默认的内存请求和限制
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# cat memory-defaults.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: LimitRange
metadata:
name: mem-limit-range
spec:
limits:
- default:
memory: 512Mi
defaultRequest:
memory: 256Mi
type: Container
default类似于之前的limit;defaultRequest类似于之前的request。
应用如下:
kubectl create -f memory-defaults.yaml –namespace=default-mem-example
命名空间default-mem-example已提前创建完毕
现在,如果在 default-mem-example 命名空间创建容器,并且该容器没有声明自己的内存请求和限制值,那么它将被指定一个默认的内存请求256 MiB和一个默认的内存限制512 Mib。
为命名空间配置默认的CPU请求和限制 示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# cpu-defaults.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: LimitRange
metadata:
name: cpu-limit-range
spec:
limits:
- default:
cpu: 1
defaultRequest:
cpu: 0.5
type: Container
应用如下:
kubectl create -f cpu-defaults.yaml –namespace=default-cpu-example 其中default-cpu-example名称空间已被提前创建
现在如果在 default-cpu-example 命名空间创建一个容器,该容器没有声明自己的 CPU 请求和限制时,那么将会给它指定默认的 CPU 请求0.5和默认的 CPU 限制值1。
配置命名空间的最小和最大内存约束
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# cat memory-constraints.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: LimitRange
metadata:
name: mem-min-max-demo-lr
spec:
limits:
- max:
memory: 1Gi
min:
memory: 500Mi
type: Container
应用如下:
kubectl create -f memory-constraints.yaml –namespace=constraints-mem-example
其中constraints-mem-example名称空间已被提前创建
查看 LimitRange 的详情:
kubectl get limitrange mem-min-max-demo-lr –namespace=constraints-mem-example –output=yaml
输出显示预期的最小和最大内存约束。但请注意,即使您没有在 LimitRange 的配置文件中指定默认值,默认值也会被自动创建。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
limits:
- default:
memory: 1Gi
defaultRequest:
memory: 1Gi
max:
memory: 1Gi
min:
memory: 500Mi
type: Container
现在,只要在 constraints-mem-example 命名空间中创建容器,Kubernetes 就会执行下面的步骤:
-
如果 Container 未指定自己的内存请求和限制,将为它指定默认的内存请求和限制
-
验证 Container 的内存请求是否大于或等于500 MiB【超出范围容器创建失败】
-
验证 Container 的内存限制是否小于或等于1 GiB【超出范围容器创建失败】
配置命名空间的最小和最大CPU约束
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# cpu-constraints.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: LimitRange
metadata:
name: cpu-min-max-demo-lr
spec:
limits:
- max:
cpu: "800m"
min:
cpu: "200m"
type: Container
应用如下:
kubectl create -f cpu-constraints.yaml –namespace=constraints-cpu-example
其中constraints-cpu-example名称空间已被提前创建
查看 LimitRange 详情:
kubectl get limitrange cpu-min-max-demo-lr –output=yaml –namespace=constraints-cpu-example
输出结果显示 CPU 的最小和最大限制符合预期。但需要注意的是,尽管你在 LimitRange 的配置文件中你没有声明默认值,默认值也会被自动创建。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
limits:
- default:
cpu: 800m
defaultRequest:
cpu: 800m
max:
cpu: 800m
min:
cpu: 200m
type: Container
现在不管什么时候在 constraints-cpu-example 命名空间中创建容器,Kubernetes 都会执行下面这些步骤:
- 如果容器没有声明自己的 CPU 请求和限制,将为容器指定默认 CPU 请求和限制。
- 核查容器声明的 CPU 请求确保其大于或者等于200 millicpu。
- 核查容器声明的 CPU 限制确保其小于或者等于800 millicpu。
配置命名空间下pod总数
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# cat quota-pod.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: pod-demo
spec:
hard:
pods: "2"
应用如下【命名空间quota-pod-example已提前创建完毕】:
kubectl apply -f quota-pod.yaml –namespace=quota-pod-example
查看资源配额的详细信息:
kubectl get resourcequota pod-demo –namespace=quota-pod-example –output=yaml
从输出的信息我们可以看到,该命名空间下pod的配额是2个,目前创建的pods数为0,配额使用率为0。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
spec:
hard:
pods: "2"
status:
hard:
pods: "2"
used:
pods: "0"
4.Pod资源限制
4.1.CPU计量单位
在centos当中的获取cpu信息shell脚本:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
#!/bin/bash
#Processor_CPU:逻辑cpu的信息
#Physical_CPU:物理cpu的信息
#Cores_CPU:cpu的核心信息
if [ -f /proc/cpuinfo ]
then
Processor_CPU=$(cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "processor" )
echo "-------------"
echo "$Processor_CPU"
Physical_CPU=$(cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "physical id" )
echo "-------------"
echo "$Physical_CPU"
Cores_CPU=$(cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "core id" )
echo "-------------"
echo "$Cores_CPU"
else
echo " file /proc/cpuinfo is not exsit"
fi
[root@k8s-master ingress]# chmod 777 cpu.sh
[root@k8s-master ingress]# ./cpu.sh
# 运行结果
-------------
processor : 0
processor : 1
processor : 2
processor : 3
-------------
physical id : 0
physical id : 0
physical id : 1
physical id : 1
-------------
core id : 0
core id : 1
core id : 0
core id : 1
#这里可以看出cpu为两个物理CPU,两个核心,四个逻辑CPU
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Kubernetes 中的一个 cpu 等于:
1 AWS vCPU
1 GCP Core
1 Azure vCore
1 Hyperthread (intel处理器)
这里物理使用的CPU是interl的处理器,1 Hyperthread 是指我们获取到Porcess_CPU的信息,判断cpu是能够超线程工作,CORE的数量小于Porecessor数量,且Porcessor的数量是core两倍。
k8s当中支持cpu的浮点数,1CPU= 1000 millicore,0.5CPU= 500millicore。
物理CPU,物理CPU内核,逻辑CPU概念详解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
1.说明
CPU(Central Processing Unit)是中央处理单元,
本文介绍物理CPU,物理CPU内核,逻辑CPU,
以及他们三者之间的关系,
一个物理CPU可以有1个或者多个物理内核,
一个物理内核可以作为1个或者2个逻辑CPU。
2.物理CPU
物理CPU就是计算机上实际安装的CPU,
物理CPU数就是主板上实际插入的CPU数量。
在Linux上查看/proc/cpuinfo,
其中的physical id就是每个物理CPU的id,
有几个不同的physical id就有几个物理CPU。
3.物理CPU内核
每颗物理CPU可以有1个或者多个物理内核,
通常每颗物理CPU的内核数都是固定的,
单核CPU就是有1个物理内核,
双核CPU就是有2个物理内核。
在Linux上查看/proc/cpuinfo,
其中的core id就是每颗物理CPU的物理内核id,
有几个不同的core id就有几个物理内核。
总的CPU物理内核数 = 物理CPU数 * 每颗物理CPU的内核数
4.逻辑CPU
操作系统可以使用逻辑CPU来模拟真实CPU。
在没有多核处理器的时候,
一个物理CPU只能有一个物理内核,
而现在有了多核技术,
一个物理CPU可以有多个物理内核,
可以把一个CPU当作多个CPU使用,
也就是所谓的逻辑CPU。
没有开启超线程时,逻辑CPU的个数就是总的CPU物理内核数。
然而开启超线程后,逻辑CPU的个数就是总的CPU物理内核数的两倍。
在Linux上查看/proc/cpuinfo,
其中的processor就是逻辑CPU,
有几个processor就有几个逻辑CPU。
总的逻辑CPU数 = 物理CPU个数 * 每颗物理CPU的核数 * 超线程数
总的逻辑CPU数 = 总的CPU物理内核数 * 超线程数
5.几核几线程
基于上面的基本概念,
理解一下常说的几核几线程。
如果计算机有一个物理CPU,
是双核的,支持超线程。
那么这台计算机就是双核四线程。
实际上几核几线程中的线程数就是逻辑CPU数。
对于两路四核超线程计算机,
两路指计算机有2个物理CPU,
每颗CPU中有4个物理内核,
CPU支持超线程,
就有242=16个逻辑CPU,
这就是通常所谓的16核计算机。
6.两路四核超线程
实际能看到的2个物理CPU:
linux下查看cpu信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
#linux下查看cpu信息可以用 cat /proc/cpuinfo 指令
# 总核数 = 物理CPU个数 X 每颗物理CPU的核数
# 总逻辑CPU数 = 物理CPU个数 X 每颗物理CPU的核数 X 超线程数
# 查看物理CPU个数
cat /proc/cpuinfo| grep "physical id"| sort| uniq| wc -l
# 查看每个物理CPU中core的个数
cat /proc/cpuinfo| grep "cpu cores"| uniq
# 查看逻辑CPU的个数
cat /proc/cpuinfo| grep "processor"| wc -l
4.2.内存计量单位
memory计量单位
内存的计量单位为字节计算,可以直接用字节数字表示,但是这样表示不能直观的显示内存的大小,可以使用E, P, T, G, M, K,后缀表示,10^3k=1M 。也可以使幂数:Ei,Pi,Ti ,Gi,Mi,Ki表示,2^10Ki =1 Mi。
4.3.limits与requests
limits:表示控制pod对资源的最大的请求量.
requests:表示运行此pod需要分配的系统资源
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
---
apiVerion: v1
kind:pod
...
...
spec:
contianers:
- name: res_test
...
resource:
limits:
cpu: 0.25m
memory: 200Mi
requests:
cpu: 0.25m
memory: 200Mi
4.4.Qos Class(quality of service)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
分配类资源限制之后,describe pod时会生成三个资源类
Qos(quality of service (服务质量)) class:
Qos class:
Guaranteed(保证值): 同时设置cpu和内存的limits和requests
Burstable(可供使用): 至少有一个容器设置cpu和内存的requests属性
BestEffort(尽力而为): 没有一个容器设置了资源限制
优先级:guaranteed > Burstable > BestEffort
当系统资源不够用时,会终止低优先级的pod。
pod qosClass介绍
qosClass 表示服务质量类型(Quality of Service)。其值由pod请求的内存和cpu确定的,有三种类型:Guaranteed,Burstable 和 BestEffort。当node资源不足而驱逐pod时优先级不同:BestEffort→Burstable→Guaranteed。最先驱逐BestEffort,然后Burstable,最后Guaranteed。pod没有配置资源限制的时默认为BestEffort。
1
kubectl get pod [pod名称] -o yml podqosClass类型
输出中
qosClass字段显示当前
QoS Classes分类
Guranteed:pod中所有Container的所有Resource的limit和request都相等且不为0,则这个Pod的QoS Class就是Guaranteed。注意,如果一个容器只指明了limit,而未指明request,则表明request的值等于limit的值。
Burstable:pod中至少有一个容器设置CPU或内存资源的requests属性。
BestEffort:Pod中没有任何一个容器设置了requests或limits属性。
node资源紧缺时pod驱逐机制
1
Guaranteed > Burstable > BestEffort
QoS(服务质量等级)
是作用在 Pod 上的一个配置,当 Kubernetes 创建一个 Pod 时,它就会给这个 Pod 分配一个 QoS 等级,可以是以下等级之一:
- Guaranteed:同时设置了CPU和内存的
requests和limits而且值必须相等。(这类的pod是最高优先级) - Burstable:pod至少有一个容器设置了cpu或内存的
requests和limits,且不满足 Guarantee 等级的要求。即内存或CPU的值设置的不同。(中等优先级) - BestEffort:没有任何一个容器设置了
requests或limits的属性。(最低优先级)
Guaranteed样例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-demo
namespace: default
labels:
name: myapp
tier: appfront
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp
image: ikubernetes/myapp:v2
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "500m"
limits:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "500m"
结果:
1
2
3
4
$ kubectl describe pod my-demo
......
QoS Class: Guaranteed
......
Burstable样例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-demo02
namespace: default
labels:
name: myapp
tier: appfront
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp
image: ikubernetes/myapp:v2
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
memory: "256Mi"
cpu: "200m"
limits:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "500m"
结果:
1
2
3
4
$ kubectl describe pod my-demo02
....
QoS Class: Burstable
....
BestEffort样例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-demo03
namespace: default
labels:
name: myapp
tier: appfront
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp
image: ikubernetes/myapp:v2
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
结果:
1
2
3
4
$ kubectl describe pod my-demo03
....
QoS Class: BestEffort
....
5.常用命令
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
# 使用kubectl top node 查看资源使用情况
[root@master 1.8+]# kubectl top node
NAME CPU(cores) CPU% MEMORY(bytes) MEMORY%
master 98m 4% 1067Mi 62%
node1 27m 1% 727Mi 42%
node2 34m 1% 800Mi 46%
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl describe node k8s-node1
Name: k8s-node1
Roles: <none>
Labels: beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64
beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux
kubernetes.io/arch=amd64
kubernetes.io/hostname=k8s-node1
kubernetes.io/os=linux
Annotations: kubeadm.alpha.kubernetes.io/cri-socket: /var/run/dockershim.sock
node.alpha.kubernetes.io/ttl: 0
projectcalico.org/IPv4Address: 172.51.216.82/24
projectcalico.org/IPv4IPIPTunnelAddr: 10.244.36.64
volumes.kubernetes.io/controller-managed-attach-detach: true
CreationTimestamp: Tue, 17 Aug 2021 12:45:38 +0800
Taints: <none>
Unschedulable: false
Lease:
HolderIdentity: k8s-node1
AcquireTime: <unset>
RenewTime: Sun, 24 Oct 2021 20:32:41 +0800
Conditions:
Type Status LastHeartbeatTime LastTransitionTime Reason Message
---- ------ ----------------- ------------------ ------ -------
NetworkUnavailable False Mon, 11 Oct 2021 17:25:22 +0800 Mon, 11 Oct 2021 17:25:22 +0800 CalicoIsUp Calico is running on this node
MemoryPressure False Sun, 24 Oct 2021 20:32:03 +0800 Thu, 19 Aug 2021 16:36:39 +0800 KubeletHasSufficientMemory kubelet has sufficient memory available
DiskPressure False Sun, 24 Oct 2021 20:32:03 +0800 Thu, 19 Aug 2021 16:36:39 +0800 KubeletHasNoDiskPressure kubelet has no disk pressure
PIDPressure False Sun, 24 Oct 2021 20:32:03 +0800 Thu, 19 Aug 2021 16:36:39 +0800 KubeletHasSufficientPID kubelet has sufficient PID available
Ready True Sun, 24 Oct 2021 20:32:03 +0800 Thu, 19 Aug 2021 16:36:39 +0800 KubeletReady kubelet is posting ready status
Addresses:
InternalIP: 172.51.216.82
Hostname: k8s-node1
Capacity:
cpu: 4
ephemeral-storage: 51175Mi
hugepages-2Mi: 0
memory: 16247300Ki
pods: 110
Allocatable:
cpu: 4
ephemeral-storage: 48294789041
hugepages-2Mi: 0
memory: 16144900Ki
pods: 110
System Info:
Machine ID: 1e80dfab70f54f4d8222902d8db7d604
System UUID: 1e80dfab70f54f4d8222902d8db7d604
Boot ID: 9e432adc-616c-4225-af4c-7ea4854fb6e3
Kernel Version: 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64
OS Image: CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
Operating System: linux
Architecture: amd64
Container Runtime Version: docker://19.3.15
Kubelet Version: v1.20.6
Kube-Proxy Version: v1.20.6
PodCIDR: 10.244.1.0/24
PodCIDRs: 10.244.1.0/24
Non-terminated Pods: (5 in total)
Namespace Name CPU Requests CPU Limits Memory Requests Memory Limits AGE
--------- ---- ------------ ---------- --------------- ------------- ---
ingress-nginx ingress-nginx-admission-create-nzs4l 100m (2%) 0 (0%) 90Mi (0%) 0 (0%) 40d
kube-system calico-node-svzpr 250m (6%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 68d
kube-system coredns-7f89b7bc75-xcn97 100m (2%) 0 (0%) 70Mi (0%) 170Mi (1%) 68d
kube-system kube-proxy-h6v7c 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 68d
kube-system metrics-server-9c7dc6fdc-mgl6r 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 2d4h
Allocated resources:
(Total limits may be over 100 percent, i.e., overcommitted.)
Resource Requests Limits
-------- -------- ------
cpu 450m (11%) 0 (0%)
memory 160Mi (1%) 170Mi (1%)
ephemeral-storage 0 (0%) 0 (0%)
hugepages-2Mi 0 (0%) 0 (0%)
Events: <none>
# 查看pod资源
[root@master 1.8+]# kubectl top pod -n kube-system
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
coredns-6955765f44-7ptsb 3m 9Mi
coredns-6955765f44-vcwr5 3m 8Mi
etcd-master 14m 145Mi
# 查看hpa
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl get hpa -n dev
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 0%/3% 1 10 1 32s
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get deploy -n dev -w
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
myapp 1/1 1 1 21m
myapp 1/3 1 1 28m
myapp 1/3 1 1 28m
myapp 1/3 1 1 28m
myapp 1/3 3 1 28m
myapp 2/3 3 2 28m
myapp 3/3 3 3 28m
myapp 3/1 3 3 34m
myapp 3/1 3 3 34m
myapp 1/1 1 1 34m
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
myapp-54886948c5-c6gm2 1/1 Running 0 21m
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 Pending 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 Pending 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 Pending 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 Pending 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 1/1 Running 0 1s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 1/1 Running 0 1s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 1/1 Terminating 0 5m52s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 1/1 Terminating 0 5m52s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 1/1 Terminating 0 5m52s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 1/1 Terminating 0 5m52s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 Terminating 0 5m53s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 Terminating 0 5m53s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 Terminating 0 5m54s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 Terminating 0 5m54s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 Terminating 0 6m3s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 Terminating 0 6m3s
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get hpa -n dev -w
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 0%/3% 1 10 1 14m
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 7%/3% 1 10 1 20m
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 7%/3% 1 10 3 20m
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 0%/3% 1 10 3 21m
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 0%/3% 1 10 3 25m
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 0%/3% 1 10 1 26m
二、基础
在前面的课程中,我们已经可以实现通过手工执行kubectl scale命令实现Pod扩容或缩容,但是这显然不符合Kubernetes的定位目标–自动化、智能化。 Kubernetes期望可以实现通过监测Pod的使用情况,实现pod数量的自动调整,于是就产生了Horizontal Pod Autoscaler(HPA)这种控制器。
HPA可以获取每个Pod利用率,然后和HPA中定义的指标进行对比,同时计算出需要伸缩的具体值,最后实现Pod的数量的调整。其实HPA与之前的Deployment一样,也属于一种Kubernetes资源对象,它通过追踪分析RC控制的所有目标Pod的负载变化情况,来确定是否需要针对性地调整目标Pod的副本数,这是HPA的实现原理。
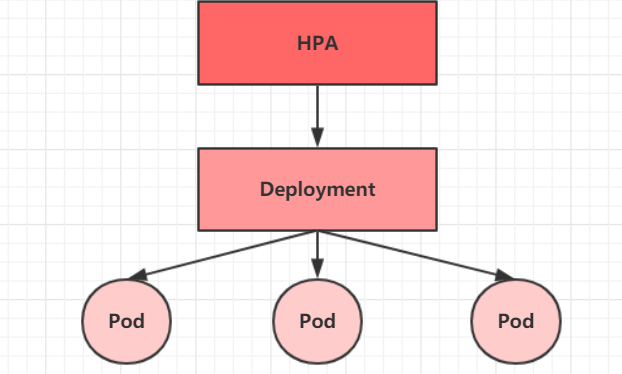
接下来,我们来做一个实验
1 安装metrics-server
metrics-server可以用来收集集群中的资源使用情况
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# 安装git
[root@master ~]# yum install git -y
# 获取metrics-server, 注意使用的版本
[root@master ~]# git clone -b v0.3.6 https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/metrics-server
# 修改deployment, 注意修改的是镜像和初始化参数
[root@master ~]# cd /root/metrics-server/deploy/1.8+/
[root@master 1.8+]# vim metrics-server-deployment.yaml
# 按图中添加下面选项
hostNetwork: true
image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/metrics-server-amd64:v0.3.6
args:
- --kubelet-insecure-tls
- --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,Hostname,InternalDNS,ExternalDNS,ExternalIP
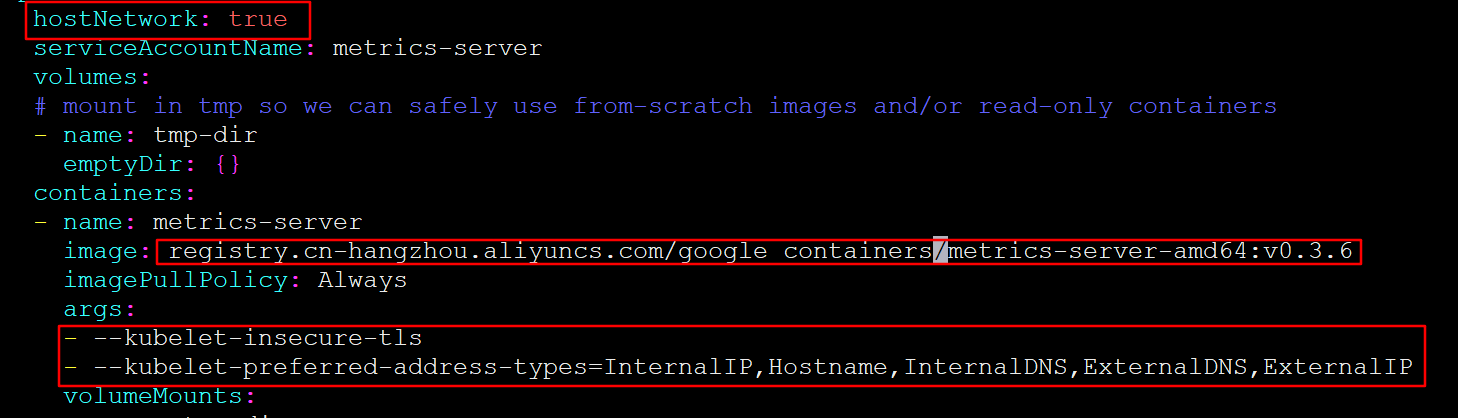
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 安装metrics-server
[root@master 1.8+]# kubectl apply -f ./
# 查看pod运行情况
[root@master 1.8+]# kubectl get pod -n kube-system
metrics-server-6b976979db-2xwbj 1/1 Running 0 90s
# 使用kubectl top node 查看资源使用情况
[root@master 1.8+]# kubectl top node
NAME CPU(cores) CPU% MEMORY(bytes) MEMORY%
master 98m 4% 1067Mi 62%
node1 27m 1% 727Mi 42%
node2 34m 1% 800Mi 46%
[root@master 1.8+]# kubectl top pod -n kube-system
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
coredns-6955765f44-7ptsb 3m 9Mi
coredns-6955765f44-vcwr5 3m 8Mi
etcd-master 14m 145Mi
...
# 至此,metrics-server安装完成
2 准备deployment和servie
为了操作简单,直接使用命令
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 创建deployment
[root@master 1.8+]# kubectl run nginx --image=nginx:latest --requests=cpu=100m -n dev
# 创建service
[root@master 1.8+]# kubectl expose deployment nginx --type=NodePort --port=80 -n dev
# 查看
[root@master 1.8+]# kubectl get deployment,pod,svc -n dev
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/nginx 1/1 1 1 47s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-7df9756ccc-bh8dr 1/1 Running 0 47s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/nginx NodePort 10.109.57.248 <none> 80:31136/TCP 35s
3 部署HPA
创建pc-hpa.yaml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
apiVersion: autoscaling/v1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: pc-hpa
namespace: dev
spec:
minReplicas: 1 #最小pod数量
maxReplicas: 10 #最大pod数量
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 3 # CPU使用率指标
scaleTargetRef: # 指定要控制的nginx信息
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: nginx
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 创建hpa
[root@master 1.8+]# kubectl create -f pc-hpa.yaml
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/pc-hpa created
# 查看hpa
[root@master 1.8+]# kubectl get hpa -n dev
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
pc-hpa Deployment/nginx 0%/3% 1 10 1 62s
4 测试
使用压测工具对service地址192.168.109.100:31136进行压测,然后通过控制台查看hpa和pod的变化
hpa变化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
[root@master ~]# kubectl get hpa -n dev -w
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
pc-hpa Deployment/nginx 0%/3% 1 10 1 4m11s
pc-hpa Deployment/nginx 0%/3% 1 10 1 5m19s
pc-hpa Deployment/nginx 22%/3% 1 10 1 6m50s
pc-hpa Deployment/nginx 22%/3% 1 10 4 7m5s
pc-hpa Deployment/nginx 22%/3% 1 10 8 7m21s
pc-hpa Deployment/nginx 6%/3% 1 10 8 7m51s
pc-hpa Deployment/nginx 0%/3% 1 10 8 9m6s
pc-hpa Deployment/nginx 0%/3% 1 10 8 13m
pc-hpa Deployment/nginx 0%/3% 1 10 1 14m
deployment变化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[root@master ~]# kubectl get deployment -n dev -w
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx 1/1 1 1 11m
nginx 1/4 1 1 13m
nginx 1/4 1 1 13m
nginx 1/4 1 1 13m
nginx 1/4 4 1 13m
nginx 1/8 4 1 14m
nginx 1/8 4 1 14m
nginx 1/8 4 1 14m
nginx 1/8 8 1 14m
nginx 2/8 8 2 14m
nginx 3/8 8 3 14m
nginx 4/8 8 4 14m
nginx 5/8 8 5 14m
nginx 6/8 8 6 14m
nginx 7/8 8 7 14m
nginx 8/8 8 8 15m
nginx 8/1 8 8 20m
nginx 8/1 8 8 20m
nginx 1/1 1 1 20m
pod变化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
[root@master ~]# kubectl get pods -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-7df9756ccc-bh8dr 1/1 Running 0 11m
nginx-7df9756ccc-cpgrv 0/1 Pending 0 0s
nginx-7df9756ccc-8zhwk 0/1 Pending 0 0s
nginx-7df9756ccc-rr9bn 0/1 Pending 0 0s
nginx-7df9756ccc-cpgrv 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
nginx-7df9756ccc-8zhwk 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
nginx-7df9756ccc-rr9bn 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
nginx-7df9756ccc-m9gsj 0/1 Pending 0 0s
nginx-7df9756ccc-g56qb 0/1 Pending 0 0s
nginx-7df9756ccc-sl9c6 0/1 Pending 0 0s
nginx-7df9756ccc-fgst7 0/1 Pending 0 0s
nginx-7df9756ccc-g56qb 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
nginx-7df9756ccc-m9gsj 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
nginx-7df9756ccc-sl9c6 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
nginx-7df9756ccc-fgst7 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
nginx-7df9756ccc-8zhwk 1/1 Running 0 19s
nginx-7df9756ccc-rr9bn 1/1 Running 0 30s
nginx-7df9756ccc-m9gsj 1/1 Running 0 21s
nginx-7df9756ccc-cpgrv 1/1 Running 0 47s
nginx-7df9756ccc-sl9c6 1/1 Running 0 33s
nginx-7df9756ccc-g56qb 1/1 Running 0 48s
nginx-7df9756ccc-fgst7 1/1 Running 0 66s
nginx-7df9756ccc-fgst7 1/1 Terminating 0 6m50s
nginx-7df9756ccc-8zhwk 1/1 Terminating 0 7m5s
nginx-7df9756ccc-cpgrv 1/1 Terminating 0 7m5s
nginx-7df9756ccc-g56qb 1/1 Terminating 0 6m50s
nginx-7df9756ccc-rr9bn 1/1 Terminating 0 7m5s
nginx-7df9756ccc-m9gsj 1/1 Terminating 0 6m50s
nginx-7df9756ccc-sl9c6 1/1 Terminating 0 6m50s
三、实践
HPA(Horizontal Pod Autoscaler)在k8s集群中用于POD水平自动伸缩,它是基于CPU和内存利用率对Deployment和Replicaset控制器中的pod数量进行自动扩缩容(除了CPU和内存利用率之外,也可以基于其他应程序提供的度量指标custom metrics进行自动扩缩容)。pod自动缩放不适用于无法缩放的对象,比如DaemonSets。HPA由Kubernetes API资源和控制器实现。资源决定了控制器的行为,控制器会周期性的获取CPU和内存利用率,并与目标值相比较后来调整replication controller或deployment中的副本数量。
HPA使用前提条件:
- 集群中部署了Metrics Server插件, 可以获取到Pod的CPU和内存利用率。
- Pod部署的Yaml文件中必须设置资源限制和资源请求。
1.安装metrics-server
metrics-server可以用来收集集群中的资源使用情况
https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server
安装
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 获取metrics-server, 注意使用的版本
[root@k8s-master hpa]# git clone -b v0.3.6 https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/metrics-server
# 修改deployment, 注意修改的是镜像和初始化参数
[root@k8s-master 1.8+]# cd /k8s/hpa/metrics-server/deploy/1.8+
[root@k8s-master 1.8+]# ll
total 28
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 393 Oct 22 15:18 aggregated-metrics-reader.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 308 Oct 22 15:18 auth-delegator.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 329 Oct 22 15:18 auth-reader.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 298 Oct 22 15:18 metrics-apiservice.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 804 Oct 22 15:18 metrics-server-deployment.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 291 Oct 22 15:18 metrics-server-service.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 517 Oct 22 15:18 resource-reader.yaml
[root@master 1.8+]# vim metrics-server-deployment.yaml
按图中添加下面选项
hostNetwork: true
image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/metrics-server-amd64:v0.3.6
args:
- --kubelet-insecure-tls
- --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,Hostname,InternalDNS,ExternalDNS,ExternalIP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
# 安装metrics-server
root@k8s-master 1.8+]# kubectl apply -f ./
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:aggregated-metrics-reader configured
Warning: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 ClusterRoleBinding is deprecated in v1.17+, unavailable in v1.22+; use rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 ClusterRoleBinding
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metrics-server:system:auth-delegator configured
Warning: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 RoleBinding is deprecated in v1.17+, unavailable in v1.22+; use rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 RoleBinding
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metrics-server-auth-reader configured
Warning: apiregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1 APIService is deprecated in v1.19+, unavailable in v1.22+; use apiregistration.k8s.io/v1 APIService
apiservice.apiregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1.metrics.k8s.io configured
serviceaccount/metrics-server configured
deployment.apps/metrics-server created
service/metrics-server configured
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:metrics-server configured
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:metrics-server configured
# 查看pod运行情况
[root@k8s-master 1.8+]# kubectl get pod -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
...
metrics-server-9c7dc6fdc-mgl6r 1/1 Running 0 30s
# 使用kubectl top node 查看资源使用情况
[root@k8s-master 1.8+]# kubectl top node
NAME CPU(cores) CPU% MEMORY(bytes) MEMORY%
k8s-master 538m 13% 4106Mi 26%
k8s-node1 298m 7% 2114Mi 13%
k8s-node2 303m 7% 1643Mi 10%
k8s-node3 288m 7% 1950Mi 12%
[root@k8s-master 1.8+]# kubectl top pod -n kube-system
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
calico-kube-controllers-5f6cfd688c-2tlm5 3m 31Mi
calico-node-2kgrn 34m 99Mi
calico-node-4hmgw 23m 101Mi
calico-node-svzpr 28m 103Mi
calico-node-sxlrj 28m 105Mi
coredns-7f89b7bc75-m84rp 2m 14Mi
coredns-7f89b7bc75-xcn97 2m 15Mi
etcd-k8s-master 13m 287Mi
kube-apiserver-k8s-master 47m 439Mi
kube-controller-manager-k8s-master 11m 58Mi
kube-proxy-8gwpb 1m 17Mi
kube-proxy-dbntt 1m 17Mi
kube-proxy-h6v7c 1m 16Mi
kube-proxy-xprl7 1m 19Mi
kube-scheduler-k8s-master 3m 23Mi
metrics-server-9c7dc6fdc-mgl6r 1m 12Mi
# 至此,metrics-server安装完成
2.安装ab压力测试工具
1.ab(apache benchmark)安装
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
# yum -y install httpd-tools
[root@k8s-master 1.8+]# yum -y install httpd-tools
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Determining fastest mirrors
* base: mirrors.bupt.edu.cn
* extras: mirrors.bfsu.edu.cn
* updates: mirrors.bupt.edu.cn
base | 3.6 kB 00:00:00
docker-ce-stable | 3.5 kB 00:00:00
extras | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
kubernetes | 1.4 kB 00:00:00
updates | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
updates/7/x86_64/primary_db | 12 MB 00:00:07
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package httpd-tools.x86_64 0:2.4.6-97.el7.centos.1 will be installed
--> Processing Dependency: libaprutil-1.so.0()(64bit) for package: httpd-tools-2.4.6-97.el7.centos.1.x86_64
--> Processing Dependency: libapr-1.so.0()(64bit) for package: httpd-tools-2.4.6-97.el7.centos.1.x86_64
--> Running transaction check
---> Package apr.x86_64 0:1.4.8-7.el7 will be installed
---> Package apr-util.x86_64 0:1.5.2-6.el7 will be installed
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
==========================================================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
==========================================================================================================================
Installing:
httpd-tools x86_64 2.4.6-97.el7.centos.1 updates 93 k
Installing for dependencies:
apr x86_64 1.4.8-7.el7 base 104 k
apr-util x86_64 1.5.2-6.el7 base 92 k
Transaction Summary
==========================================================================================================================
Install 1 Package (+2 Dependent packages)
Total download size: 289 k
Installed size: 584 k
Downloading packages:
(1/3): apr-1.4.8-7.el7.x86_64.rpm | 104 kB 00:00:00
(2/3): httpd-tools-2.4.6-97.el7.centos.1.x86_64.rpm | 93 kB 00:00:00
(3/3): apr-util-1.5.2-6.el7.x86_64.rpm | 92 kB 00:00:01
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 252 kB/s | 289 kB 00:00:01
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
Installing : apr-1.4.8-7.el7.x86_64 1/3
Installing : apr-util-1.5.2-6.el7.x86_64 2/3
Installing : httpd-tools-2.4.6-97.el7.centos.1.x86_64 3/3
Verifying : apr-1.4.8-7.el7.x86_64 1/3
Verifying : apr-util-1.5.2-6.el7.x86_64 2/3
Verifying : httpd-tools-2.4.6-97.el7.centos.1.x86_64 3/3
Installed:
httpd-tools.x86_64 0:2.4.6-97.el7.centos.1
Dependency Installed:
apr.x86_64 0:1.4.8-7.el7 apr-util.x86_64 0:1.5.2-6.el7
Complete!
2.ab测试的命令参数
- 命令:
ab或ab -help - 显示命令参数如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
[root@k8s-master 1.8+]# ab
ab: wrong number of arguments
Usage: ab [options] [http[s]://]hostname[:port]/path
Options are:
-n requests Number of requests to perform
-c concurrency Number of multiple requests to make at a time
-t timelimit Seconds to max. to spend on benchmarking
This implies -n 50000
-s timeout Seconds to max. wait for each response
Default is 30 seconds
-b windowsize Size of TCP send/receive buffer, in bytes
-B address Address to bind to when making outgoing connections
-p postfile File containing data to POST. Remember also to set -T
-u putfile File containing data to PUT. Remember also to set -T
-T content-type Content-type header to use for POST/PUT data, eg.
'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
Default is 'text/plain'
-v verbosity How much troubleshooting info to print
-w Print out results in HTML tables
-i Use HEAD instead of GET
-x attributes String to insert as table attributes
-y attributes String to insert as tr attributes
-z attributes String to insert as td or th attributes
-C attribute Add cookie, eg. 'Apache=1234'. (repeatable)
-H attribute Add Arbitrary header line, eg. 'Accept-Encoding: gzip'
Inserted after all normal header lines. (repeatable)
-A attribute Add Basic WWW Authentication, the attributes
are a colon separated username and password.
-P attribute Add Basic Proxy Authentication, the attributes
are a colon separated username and password.
-X proxy:port Proxyserver and port number to use
-V Print version number and exit
-k Use HTTP KeepAlive feature
-d Do not show percentiles served table.
-S Do not show confidence estimators and warnings.
-q Do not show progress when doing more than 150 requests
-g filename Output collected data to gnuplot format file.
-e filename Output CSV file with percentages served
-r Don't exit on socket receive errors.
-h Display usage information (this message)
-Z ciphersuite Specify SSL/TLS cipher suite (See openssl ciphers)
-f protocol Specify SSL/TLS protocol
(SSL3, TLS1, TLS1.1, TLS1.2 or ALL)
- ab [可选的参数选项] 需要进行压力测试的url
- 参数说明:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
此外,我们再根据上面的用法介绍界面来详细了解每个参数选项的作用。
-n 即requests,用于指定压力测试总共的执行次数。
-c 即concurrency,用于指定的并发数。
-t 即timelimit,等待响应的最大时间(单位:秒)。
-b 即windowsize,TCP发送/接收的缓冲大小(单位:字节)。
-p 即postfile,发送POST请求时需要上传的文件,此外还必须设置-T参数。
-u 即putfile,发送PUT请求时需要上传的文件,此外还必须设置-T参数。
-T 即content-type,用于设置Content-Type请求头信息,例如:application/x-www-form-urlencoded,默认值为text/plain。
-v 即verbosity,指定打印帮助信息的冗余级别。
-w 以HTML表格形式打印结果。
-i 使用HEAD请求代替GET请求。
-x 插入字符串作为table标签的属性。
-y 插入字符串作为tr标签的属性。
-z 插入字符串作为td标签的属性。
-C 添加cookie信息,例如:"Apache=1234"(可以重复该参数选项以添加多个)。
-H 添加任意的请求头,例如:"Accept-Encoding: gzip",请求头将会添加在现有的多个请求头之后(可以重复该参数选项以添加多个)。
-A 添加一个基本的网络认证信息,用户名和密码之间用英文冒号隔开。
-P 添加一个基本的代理认证信息,用户名和密码之间用英文冒号隔开。
-X 指定使用的和端口号,例如:"126.10.10.3:88"。
-V 打印版本号并退出。
-k 使用HTTP的KeepAlive特性。
-d 不显示百分比。
-S 不显示预估和警告信息。
-g 输出结果信息到gnuplot格式的文件中。
-e 输出结果信息到CSV格式的文件中。
-r 指定接收到错误信息时不退出程序。
-h 显示用法信息,其实就是ab -help。
3.ab的使用
- 模拟并发请求100次,总共请求10000次
- 命令模板:
ab -c 100 -n 10000 待测试网站(建议完整路径) - 内容解释:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
Server Software: nginx/1.10.2 (服务器软件名称及版本信息)
Server Hostname: 192.168.1.106(服务器主机名)
Server Port: 80 (服务器端口)
Document Path: /index1.html. (供测试的URL路径)
Document Length: 3721 bytes (供测试的URL返回的文档大小)
Concurrency Level: 1000 (并发数)
Time taken for tests: 2.327 seconds (压力测试消耗的总时间)
Complete requests: 5000 (的总次数)
Failed requests: 688 (失败的请求数)
Write errors: 0 (网络连接写入错误数)
Total transferred: 17402975 bytes (传输的总数据量)
HTML transferred: 16275725 bytes (HTML文档的总数据量)
Requests per second: 2148.98 [#/sec] (mean) (平均每秒的请求数) 这个是非常重要的参数数值,服务器的吞吐量
Time per request: 465.338 [ms] (mean) (所有并发用户(这里是1000)都请求一次的平均时间)
Time request: 0.247 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests) (单个用户请求一次的平均时间)
Transfer rate: 7304.41 [Kbytes/sec] received 每秒获取的数据长度 (传输速率,单位:KB/s)
...
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 347 ## 50%的请求在347ms内返回
66% 401 ## 60%的请求在401ms内返回
75% 431
80% 516
90% 600
95% 846
98% 1571
99% 1593
100% 1619 (longest request)
4.压力测试(示例)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
命令: # ab -c 100 -n 5000 http://192.168.1.106/index1.html
命令:# ab -c 10000 -n 50000 http://192.168.1.106/index1.html
简单解释:并发访问量过大 服务器拒绝访问,理论上通过系统配置,可以有更好的承受能力
注意事项
- 测试机与被测试机要分开
- 不要对线上的服务器做压力测试
- 观察测试工具ab所在机器,以及被测试的前端机的CPU、内存、网络等都不超过最高限度的75%
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u011415782/article/details/78501799
3.测试1
1.准备deployment和service
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
[root@k8s-master hpa]# vim hpa-deploy.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: myapp
namespace: dev
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp
image: ikubernetes/myapp:v1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
memory: "50Mi"
cpu: "200m"
limits:
memory: "50Mi"
cpu: "200m"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: myapp
namespace: dev
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: myapp
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl apply -f hpa-deploy.yaml
deployment.apps/myapp created
service/myapp created
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl get all -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/myapp-54886948c5-c6gm2 1/1 Running 0 7s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/myapp NodePort 10.100.49.88 <none> 80:32690/TCP 7s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/myapp 1/1 1 1 7s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/myapp-54886948c5 1 1 1 7s
[root@k8s-master hpa]# curl 172.51.216.81:32690
Hello MyApp | Version: v1 | <a href="hostname.html">Pod Name</a>
2.部署HPA
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# # kubectl autoscale deployment myapp --min=1 --max=8 --cpu-percent=60
[root@k8s-master hpa]# vim pc-hpa.yaml
apiVersion: autoscaling/v1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: pc-hpa
namespace: dev
spec:
minReplicas: 1 #最小pod数量
maxReplicas: 10 #最大pod数量
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 3 #cpu使用率指标,意思是当pod使用率达到3%之后就增加新的pod
scaleTargetRef: #指定要控制的myapp信息
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: myapp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl apply -f pc-hpa.yaml
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/pc-hpa created
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl get hpa -n dev
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 0%/3% 1 10 1 32s
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl describe hpa pc-hpa -n dev
Name: pc-hpa
Namespace: dev
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
CreationTimestamp: Sat, 23 Oct 2021 21:28:13 +0800
Reference: Deployment/myapp
Metrics: ( current / target )
resource cpu on pods (as a percentage of request): 0% (0) / 3%
Min replicas: 1
Max replicas: 10
Deployment pods: 1 current / 1 desired
Conditions:
Type Status Reason Message
---- ------ ------ -------
AbleToScale True ReadyForNewScale recommended size matches current size
ScalingActive True ValidMetricFound the HPA was able to successfully calculate a replica count from cpu resource utilization (percentage of request)
ScalingLimited True TooFewReplicas the desired replica count is less than the minimum replica count
Events: <none>
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl get all -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/myapp-54886948c5-c6gm2 1/1 Running 0 13m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/myapp NodePort 10.100.49.88 <none> 80:32690/TCP 13m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/myapp 1/1 1 1 13m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/myapp-54886948c5 1 1 1 13m
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 0%/3% 1 10 1 5m4s
3.压力测试
新建窗口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# 新建三个xshell窗口,第一个检测deploy,第二个检测pod,第三个检测hpa
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get deploy -n dev -w
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
myapp 1/1 1 1 21m
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
myapp-54886948c5-c6gm2 1/1 Running 0 21m
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get hpa -n dev -w
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 0%/3% 1 10 1 14m
压力测试,验证HPA的扩缩容 使用ab命令进行压力测试,主要有两个参数: -n :总共的请求执行数,缺省是1; -c: 并发数,缺省是1;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl get pod -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
myapp-54886948c5-c6gm2 1/1 Running 0 25m
# 接下来进行压力测试
[root@k8s-master ~]# ab -c 1000 -n 500000000000 http://172.51.216.81:32690/
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: 1430300 $>
Copyright 1996 Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/
Benchmarking 172.51.216.81 (be patient)
apr_socket_recv: Connection reset by peer (104)
Total of 8242 requests completed
# 测试结果
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl get pod -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 1/1 Running 0 2m22s
myapp-54886948c5-c6gm2 1/1 Running 0 30m
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 1/1 Running 0 2m22s
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get deploy -n dev -w
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
myapp 1/1 1 1 21m
myapp 1/3 1 1 28m
myapp 1/3 1 1 28m
myapp 1/3 1 1 28m
myapp 1/3 3 1 28m
myapp 2/3 3 2 28m
myapp 3/3 3 3 28m
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
myapp-54886948c5-c6gm2 1/1 Running 0 21m
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 Pending 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 Pending 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 Pending 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 Pending 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 1/1 Running 0 1s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 1/1 Running 0 1s
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get hpa -n dev -w
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 0%/3% 1 10 1 14m
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 7%/3% 1 10 1 20m
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 7%/3% 1 10 3 20m
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 0%/3% 1 10 3 21m
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
# 等待一段时间后,缩容了
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl get pod -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
myapp-54886948c5-c6gm2 1/1 Running 0 35m
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get deploy -n dev -w
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
myapp 1/1 1 1 21m
myapp 1/3 1 1 28m
myapp 1/3 1 1 28m
myapp 1/3 1 1 28m
myapp 1/3 3 1 28m
myapp 2/3 3 2 28m
myapp 3/3 3 3 28m
myapp 3/1 3 3 34m
myapp 3/1 3 3 34m
myapp 1/1 1 1 34m
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
myapp-54886948c5-c6gm2 1/1 Running 0 21m
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 Pending 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 Pending 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 Pending 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 Pending 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 1/1 Running 0 1s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 1/1 Running 0 1s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 1/1 Terminating 0 5m52s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 1/1 Terminating 0 5m52s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 1/1 Terminating 0 5m52s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 1/1 Terminating 0 5m52s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 Terminating 0 5m53s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 Terminating 0 5m53s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 Terminating 0 5m54s
myapp-54886948c5-6m88r 0/1 Terminating 0 5m54s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 Terminating 0 6m3s
myapp-54886948c5-j5bdz 0/1 Terminating 0 6m3s
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get hpa -n dev -w
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 0%/3% 1 10 1 14m
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 7%/3% 1 10 1 20m
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 7%/3% 1 10 3 20m
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 0%/3% 1 10 3 21m
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 0%/3% 1 10 3 25m
pc-hpa Deployment/myapp 0%/3% 1 10 1 26m
4.测试2
1. 编译测试容器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
[root@k8s-master01 work]# cat kevin-t.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: kevin-t
namespace: dev
labels:
app: kevin-t
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: kevin-t
ports:
- name: http
port: 8088
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 30888
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: kevin-t
namespace: dev
spec:
replicas: 1
minReadySeconds: 10
strategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 1
maxUnavailable: 0
type: RollingUpdate
selector:
matchLabels:
app: kevin-t
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: kevin-t
spec:
containers:
- name: kevin-t
image: nginx:1.7.9
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- name: kport
containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 50Mi
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 50Mi
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","touch /tmp/health"]
livenessProbe:
exec:
command: ["test","-e","/tmp/health"]
initialDelaySeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 3
periodSeconds: 5
readinessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: kport
initialDelaySeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 3
periodSeconds: 5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
# 执行创建
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl apply -f kevin-t.yaml
# 查看pod
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl get all -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/kevin-t-6bf6d9cdb-kj5cc 0/1 Running 0 48s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/kevin-t NodePort 10.105.34.40 <none> 8088:30888/TCP 48s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/kevin-t 0/1 1 0 48s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/kevin-t-6bf6d9cdb 1 1 0 48s
# 访问
[root@k8s-master ~]# curl http://172.51.216.81:30888
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
body {
width: 35em;
margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
# 查看metrcis-service采集到的该pod的cpu和内存数据
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl top pod -n dev
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
kevin-t-6bf6d9cdb-kj5cc 2m 2Mi
# 通过上面可知,使用kevin-t的deployment控制的kevin-t的pod容器资源请求和资源限制都是100m的CPU(即0.1核)和50M的内存。当前该pod所用CPU是2m,内存是2M
2. 创建HPA限制 设置kevin-t的 deployment的最大最小副本数,HPA对应pod的CPU和内存指标做限制。
参数解释: scaleTargetRef: 要缩放的目标资源 metrics: 计算所需Pod副本数量的指标列表,每个指标单独计算,取所有计算结果的最大值作为最终副本数量 - external 引用非附属于任何对象的全局指标,可以是集群之外的组件的指标数据,如消息队列长度 - object 引用描述集群中某单一对象的特定指标,如Ingress对象上的hits-per-second等 - pods 引用当前被弹性伸缩的Pod对象的特定指标 - resource 引用资源指标,即当前被弹性伸缩的Pod对象中容器的requests和limits中定义的指标 - type 指标源的类型,可为Objects、Pods、Resource
另外注意两个指标阈值参数:
-
- targetAverageUtilization 表示的是百分比
- targetAverageValue 表示的是数值,比如100m的CPU、100Mi的内存
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
[root@k8s-master01 work]# cat kevin-t-hap.yml
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: kevin-t-hap
namespace: dev
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: kevin-t
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 3
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
targetAverageUtilization: 80
- type: Resource
resource:
name: memory
targetAverageValue: 30Mi
# 如上,设置了kevin-t的deployment控制的pod的HPA限制,当cpu使用超过设置的80%,内存使用超过30Mi时就触发自动扩容,副本数最小为1,最大为3。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl apply -f kevin-t-hap.yml
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/kevin-t-hap created
# 查看创建的HPA
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl get hpa -n dev
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
kevin-t-hap Deployment/kevin-t 2600960/30Mi, 2%/80% 1 3 1 62s
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl describe hpa kevin-t-hap -n dev
Name: kevin-t-hap
Namespace: dev
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
CreationTimestamp: Sun, 24 Oct 2021 20:11:03 +0800
Reference: Deployment/kevin-t
Metrics: ( current / target )
resource memory on pods: 2600960 / 30Mi
resource cpu on pods (as a percentage of request): 2% (2m) / 80%
Min replicas: 1
Max replicas: 3
Deployment pods: 1 current / 1 desired
Conditions:
Type Status Reason Message
---- ------ ------ -------
AbleToScale True ReadyForNewScale recommended size matches current size
ScalingActive True ValidMetricFound the HPA was able to successfully calculate a replica count from memory resource
ScalingLimited False DesiredWithinRange the desired count is within the acceptable range
Events: <none>
3. 压力测试,验证HPA的扩缩容 使用ab命令进行压力测试,主要有两个参数: -n :总共的请求执行数,缺省是1; -c: 并发数,缺省是1;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
# 测试之前kevin-t的pod是一个副本数
[root@k8s-master hpa]# kubectl get pod -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kevin-t-6bf6d9cdb-kj5cc 1/1 Running 0 22m
# 接下来进行压力测试
[root@k8s-master01 work]# ab -c 1000 -n 500000000000 http://172.51.216.81:30888/
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: 1430300 $>
Copyright 1996 Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/
Benchmarking 172.16.60.235 (be patient)
apr_socket_recv: Connection reset by peer (104)
Total of 12623 requests completed
# 发现此时,kevin-t 已经扩到2个副本了
[root@k8s-master02 ~]# kubectl get pods|grep kevin-t
kevin-t-66cdc9cdbf-5h564 1/1 Running 0 38s
kevin-t-66cdc9cdbf-jwvnv 1/1 Running 0 35m
# 再加大压力测试:
[root@k8s-master01 work]# ab -c 100 -n 50000000000000000 http://172.51.216.81:30888/
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: 1430300 $>
Copyright 1996 Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/
Benchmarking 172.16.60.235 (be patient)
# 在上面压力测试中,另外打开一个终端,发现kevin-t已经扩容到最大的3个副本了!
[root@k8s-master02 ~]# kubectl get pods|grep kevin-t
kevin-t-66cdc9cdbf-5h564 1/1 Running 0 4m52s
kevin-t-66cdc9cdbf-jwvnv 1/1 Running 0 39m
kevin-t-66cdc9cdbf-zpbfs 1/1 Running 0 80s
# 查看hpa,实时查看pod的cpu和内存状态
[root@k8s-master01 work]# kubectl get hpa -w
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
kevin-t-hap Deployment/kevin-t 4434602666m/30Mi, 1%/80% 1 3 3 19m
kevin-t-hap Deployment/kevin-t 4405930666m/30Mi, 1%/80% 1 3 3 19m
kevin-t-hap Deployment/kevin-t 4441429333m/30Mi, 1%/80% 1 3 3 20m
kevin-t-hap Deployment/kevin-t 4441429333m/30Mi, 1%/80% 1 3 3 20m
kevin-t-hap Deployment/kevin-t 4945920/30Mi, 1%/80% 1 3 2 20m
kevin-t-hap Deployment/kevin-t 4945920/30Mi, 1%/80% 1 3 2 21m
...............
# 观察kevin-t的pod情况
[root@k8s-master02 ~]# kubectl get pods|grep kevin-t -w
kevin-t-66cdc9cdbf-5h564 1/1 Running 0 11m
kevin-t-66cdc9cdbf-jwvnv 1/1 Running 0 46m
kevin-t-66cdc9cdbf-zpbfs 1/1 Running 0 7m36s
[root@k8s-master02 ~]# kubectl get pods|grep kevin-t -w
kevin-t-66cdc9cdbf-5h564 1/1 Terminating 0 12m
kevin-t-66cdc9cdbf-jwvnv 1/1 Running 0 47m
# 发现压力测试过一段时间后,随着pod的cpu和内存使用数值下降,副本数也在逐步减少到最小的1个副本
[root@k8s-master02 ~]# kubectl get pods|grep kevin-t
kevin-t-66cdc9cdbf-jwvnv 1/1 Running 0 49m


